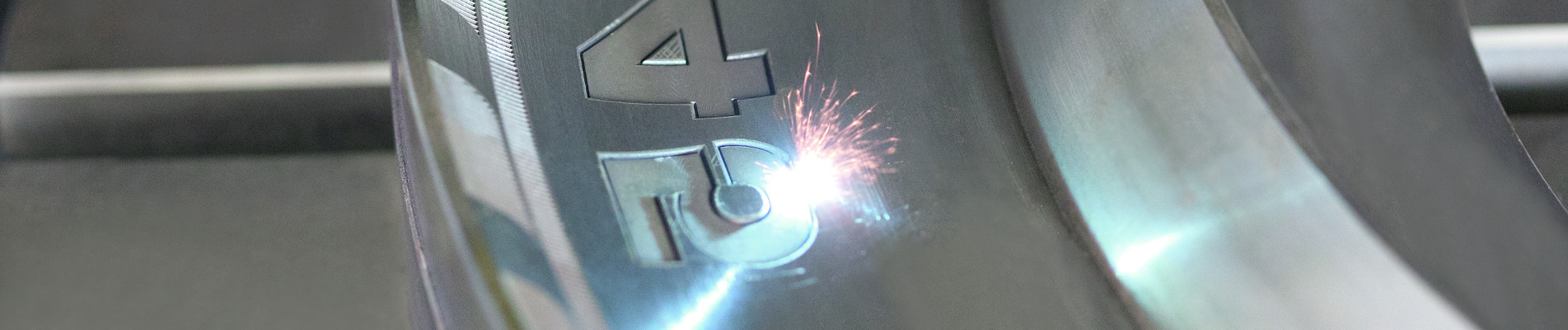
Laser engraving
Laser engraving and laser marking
 Laser engraving or laser marking is a process that constitutes a very important area of laser processing. The selected material is melted and vaporized exclusively with the help of laser light. Thus, in contrast to other engraving processes, this process takes place completely without touching the workpiece.
Laser engraving or laser marking is a process that constitutes a very important area of laser processing. The selected material is melted and vaporized exclusively with the help of laser light. Thus, in contrast to other engraving processes, this process takes place completely without touching the workpiece.
Thus, in contrast to other engraving processes, this process takes place completely without touching the workpiece.
Moreover, additional fixation of the workpiece during the entire processing of the material is not necessary.
Laser engraving and laser marking can be further subdivided into sub-processes, with one of the processes being the most suitable depending on the desired end result.

Sub-process of laser engraving and laser marking:
- Deep engraving
In deep engraving by a laser, the surface of the workpiece is ablated to depth. The laser causes melt displacement or vaporization on the workpiece. The thermal energy of the laser is thus used to selectively melt and vaporize material. This creates a clear marking on the material, the engraving. The desired engraving depth can thus be achieved very accurately and with the highest precision through targeted laser effects. - 2D and 3D laser engraving
2D, 2.5D and 3D laser engraving differ from deep engraving in that the surface of the workpiece is completely removed in depth controlled by software, whereby the material is vaporized layer by layer. In this way, the desired structure of the engraving is achieved step by step with each vaporization. In this way, an equally precise depth removal in the three-dimensional range is achieved. The range of applications for 2D, 2.5D and 3D laser engraving is very broad, so that even very complex three-dimensional surface structures can be easily created. - Micro engraving
In microengraving, workpieces are processed by ablation, which also takes place layer by layer. However, this form of engraving is characterized by the fact that both very fine linear and point-like structures can be engraved. Microengraving can thus achieve a whole new level of precision work on workpieces. - Frosting & Surface Texturing
One application is targeted "frosting". In the classic process, a protective layer is first applied to the polished impression mold. This protective layer is then removed manually again under the microscope with a scalpel from specific areas to be frosted. In contrast, frosting, which is done by a laser, is much more effective. The entire process is faster and more precise overall, as this no longer has to be done manually.
A laser can also be used to achieve defined structuring of workpiece surfaces. In this process, relatively small structural elements that are irregular or built up according to a specific geometric pattern are engraved into a smooth surface, which are then repeated continuously.
Applications of laser engraving

- Stamps and dies (for coins, medals, for certification of authenticity, etc.)
- Quality seals
- tamper-proof protective markings
- Production of chip grooves on tools
- Mold inserts
FAQ – Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Etching
What is laser engraving or laser marking?
Laser engraving or laser marking is a contactless process where material is melted and vaporized using laser light, resulting in precise and permanent engravings without needing to fix or manually process the workpiece. This method is particularly suitable for intricate structures and engravings on small or complex workpieces.
What are the sub-techniques of laser engraving?
There are various sub-techniques of laser engraving, including deep engraving, where material is removed in depth; 2D, 2.5D, and 3D laser engraving, where layers of material are vaporized; micro-engraving for very fine structures; as well as frosting and surface texturing, which create patterns or structures on the surface.
What is the difference between 2D, 2.5D, and 3D laser engraving?
The difference between 2D, 2.5D, and 3D laser engraving lies in the depth and complexity of the engraving. While 2D engraving removes material on a flat surface, 2.5D engraving can achieve slight depth variations. 3D engraving, however, allows the removal of material in multiple layers to create complex three-dimensional structures.
What is micro-engraving?
Micro-engraving is a form of laser engraving where very fine and precise lines or point structures are applied to a workpiece. It is particularly suitable for small and detailed engravings that must be executed with high precision. This technique is used in stamp engraving, forgery-proof markings, and other areas requiring the highest level of accuracy.
What are the application areas for laser engravings?
Laser engravings are used in many industries. These include the production of embossing stamps and dies for coins and medals, the engraving of seals and forgery-proof security markings, and the creation of chip breaker grooves on tools and inserts. The precision of the process also allows for very intricate and demanding engravings.
We look forward to your inquiries and will be happy to support you on the wide range of possibilities when using laser engraving.
Contact Us